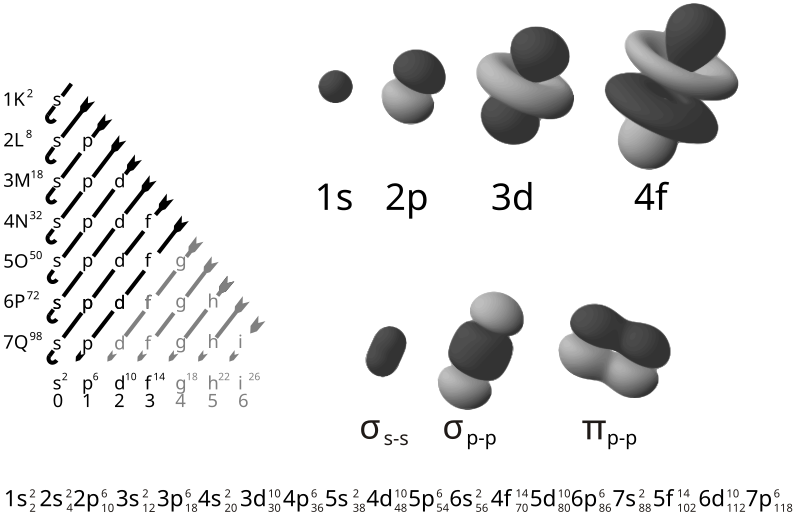
Electron Configuration
definition: A statement describing the populations of electronic energy sublevels of an atom. See the chart of electronic configurations to get the notation for all of the elements.
example: The electronic configuration of the lithium atom is 1s22s, which indicates there are two elements in the 1s sublevel and one electron in the 2s energy sublevel
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule in atomic or molecular orbitals.
According to the laws of quantum mechanics, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one orbital to another by emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.
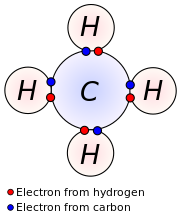
Valence Electrons
definition: An electron in an outer shell of an atom that can participate in forming chemical bonds with other atoms